无线通讯
汽车电子
汽车零部件检测
化学检测
电子烟检测
可靠性检测
电池检测
灯具检测
中国认证
亚洲认证
欧洲认证
北美认证
中东认证
澳洲认证
非洲认证
无线通讯产品注册备案
管理体系标准培训
无线类产品测试
SAR测试
OTA测试
音频/视频,信息和通信技术设备
逆变器
控制变压器和内装控制变压器的电源
医用电气设备
测量、控制和实验室用电气设备
(照明电器安规)机械
(照明电器安规)电学
智能家居产品检测
厨用家电测试
美容美发检测
日用家电检测
家用电器节能检测
汽车内外饰件(非电子电器件)—物理性能测试
汽车内外饰件(电子电器件)—IP防护
汽车电子电气件—电性能
汽车内外饰件 —机械性能测试
EMC测试
电性能测试
有害物质检测
消费品化学
生态纺织品检测
箱包鞋材检测
婴幼儿用品检测
机械类检测
温湿度及其他耐候性检测
电池检测
EMC检测
安全检测
消费品检测/通告服务-电子烟专篇
无线通讯
汽车电子
汽车零部件检测
化学检测
电子烟检测
可靠性检测
电池检测
灯具检测
中国认证
亚洲认证
欧洲认证
北美认证
中东认证
澳洲认证
非洲认证
无线通讯产品注册备案
管理体系标准培训
无线类产品测试
SAR测试
OTA测试
音频/视频,信息和通信技术设备
逆变器
控制变压器和内装控制变压器的电源
医用电气设备
测量、控制和实验室用电气设备
(照明电器安规)机械
(照明电器安规)电学
智能家居产品检测
厨用家电测试
美容美发检测
日用家电检测
家用电器节能检测
汽车内外饰件(非电子电器件)—物理性能测试
汽车内外饰件(电子电器件)—IP防护
汽车电子电气件—电性能
汽车内外饰件 —机械性能测试
EMC测试
电性能测试
有害物质检测
消费品化学
生态纺织品检测
箱包鞋材检测
婴幼儿用品检测
机械类检测
温湿度及其他耐候性检测
电池检测
EMC检测
安全检测
消费品检测/通告服务-电子烟专篇
无线通讯
汽车电子
汽车零部件检测
化学检测
电子烟检测
可靠性检测
电池检测
灯具检测
中国认证
亚洲认证
欧洲认证
北美认证
中东认证
澳洲认证
非洲认证
无线通讯产品注册备案
管理体系标准培训
无线类产品测试
SAR测试
OTA测试
音频/视频,信息和通信技术设备
逆变器
控制变压器和内装控制变压器的电源
医用电气设备
测量、控制和实验室用电气设备
(照明电器安规)机械
(照明电器安规)电学
智能家居产品检测
厨用家电测试
美容美发检测
日用家电检测
家用电器节能检测
汽车内外饰件(非电子电器件)—物理性能测试
汽车内外饰件(电子电器件)—IP防护
汽车电子电气件—电性能
汽车内外饰件 —机械性能测试
EMC测试
电性能测试
有害物质检测
消费品化学
生态纺织品检测
箱包鞋材检测
婴幼儿用品检测
机械类检测
温湿度及其他耐候性检测
电池检测
EMC检测
安全检测
消费品检测/通告服务-电子烟专篇
无线通讯
汽车电子
汽车零部件检测
化学检测
电子烟检测
可靠性检测
电池检测
灯具检测
中国认证
亚洲认证
欧洲认证
北美认证
中东认证
澳洲认证
非洲认证
无线通讯产品注册备案
管理体系标准培训
无线类产品测试
SAR测试
OTA测试
音频/视频,信息和通信技术设备
逆变器
控制变压器和内装控制变压器的电源
医用电气设备
测量、控制和实验室用电气设备
(照明电器安规)机械
(照明电器安规)电学
智能家居产品检测
厨用家电测试
美容美发检测
日用家电检测
家用电器节能检测
汽车内外饰件(非电子电器件)—物理性能测试
汽车内外饰件(电子电器件)—IP防护
汽车电子电气件—电性能
汽车内外饰件 —机械性能测试
EMC测试
电性能测试
有害物质检测
消费品化学
生态纺织品检测
箱包鞋材检测
婴幼儿用品检测
机械类检测
温湿度及其他耐候性检测
电池检测
EMC检测
安全检测
消费品检测/通告服务-电子烟专篇
无线通讯
汽车电子
汽车零部件检测
化学检测
电子烟检测
可靠性检测
电池检测
灯具检测
中国认证
亚洲认证
欧洲认证
北美认证
中东认证
澳洲认证
非洲认证
无线通讯产品注册备案
管理体系标准培训
无线类产品测试
SAR测试
OTA测试
音频/视频,信息和通信技术设备
逆变器
控制变压器和内装控制变压器的电源
医用电气设备
测量、控制和实验室用电气设备
(照明电器安规)机械
(照明电器安规)电学
智能家居产品检测
厨用家电测试
美容美发检测
日用家电检测
家用电器节能检测
汽车内外饰件(非电子电器件)—物理性能测试
汽车内外饰件(电子电器件)—IP防护
汽车电子电气件—电性能
汽车内外饰件 —机械性能测试
EMC测试
电性能测试
有害物质检测
消费品化学
生态纺织品检测
箱包鞋材检测
婴幼儿用品检测
机械类检测
温湿度及其他耐候性检测
电池检测
EMC检测
安全检测
消费品检测/通告服务-电子烟专篇
无线通讯
汽车电子
汽车零部件检测
化学检测
电子烟检测
可靠性检测
电池检测
灯具检测
中国认证
亚洲认证
欧洲认证
北美认证
中东认证
澳洲认证
非洲认证
无线通讯产品注册备案
管理体系标准培训
无线类产品测试
SAR测试
OTA测试
音频/视频,信息和通信技术设备
逆变器
控制变压器和内装控制变压器的电源
医用电气设备
测量、控制和实验室用电气设备
(照明电器安规)机械
(照明电器安规)电学
智能家居产品检测
厨用家电测试
美容美发检测
日用家电检测
家用电器节能检测
汽车内外饰件(非电子电器件)—物理性能测试
汽车内外饰件(电子电器件)—IP防护
汽车电子电气件—电性能
汽车内外饰件 —机械性能测试
EMC测试
电性能测试
有害物质检测
消费品化学
生态纺织品检测
箱包鞋材检测
婴幼儿用品检测
机械类检测
温湿度及其他耐候性检测
电池检测
EMC检测
安全检测
消费品检测/通告服务-电子烟专篇
无线通讯
汽车电子
汽车零部件检测
化学检测
电子烟检测
可靠性检测
电池检测
灯具检测
中国认证
亚洲认证
欧洲认证
北美认证
中东认证
澳洲认证
非洲认证
无线通讯产品注册备案
管理体系标准培训
无线类产品测试
SAR测试
OTA测试
音频/视频,信息和通信技术设备
逆变器
控制变压器和内装控制变压器的电源
医用电气设备
测量、控制和实验室用电气设备
(照明电器安规)机械
(照明电器安规)电学
智能家居产品检测
厨用家电测试
美容美发检测
日用家电检测
家用电器节能检测
汽车内外饰件(非电子电器件)—物理性能测试
汽车内外饰件(电子电器件)—IP防护
汽车电子电气件—电性能
汽车内外饰件 —机械性能测试
EMC测试
电性能测试
有害物质检测
消费品化学
生态纺织品检测
箱包鞋材检测
婴幼儿用品检测
机械类检测
温湿度及其他耐候性检测
电池检测
EMC检测
安全检测
消费品检测/通告服务-电子烟专篇
无线通讯
汽车电子
汽车零部件检测
化学检测
电子烟检测
可靠性检测
电池检测
灯具检测
中国认证
亚洲认证
欧洲认证
北美认证
中东认证
澳洲认证
非洲认证
无线通讯产品注册备案
管理体系标准培训
无线类产品测试
SAR测试
OTA测试
音频/视频,信息和通信技术设备
逆变器
控制变压器和内装控制变压器的电源
医用电气设备
测量、控制和实验室用电气设备
(照明电器安规)机械
(照明电器安规)电学
智能家居产品检测
厨用家电测试
美容美发检测
日用家电检测
家用电器节能检测
汽车内外饰件(非电子电器件)—物理性能测试
汽车内外饰件(电子电器件)—IP防护
汽车电子电气件—电性能
汽车内外饰件 —机械性能测试
EMC测试
电性能测试
有害物质检测
消费品化学
生态纺织品检测
箱包鞋材检测
婴幼儿用品检测
机械类检测
温湿度及其他耐候性检测
电池检测
EMC检测
安全检测
消费品检测/通告服务-电子烟专篇

资讯 | CIE发布《CIE关于干扰光与光污染的立场声明》
作者:
立讯检测集团
来源:
发布时间:
2025-12-12
国际照明委员会(CIE)近日发布《CIE关于干扰光与光污染的立场声明》第一版(CIE PS 003:2025)。以下为该立场声明的简要内容:
夜间照明的目的是提升视觉舒适度与安全性。但在照明系统的设计与实施过程中,应避免产生过度的不良影响。
本立场声明的关键要点如下:
■ Benefits of light at night夜间照明具有诸多益处
The presence of road lighting is associated with a reduction in the risk of road traffic collision at night, in particular those collisions resulting in serious or fatal injuries for vulnerable road users such as pedestrians and cyclists, and to some extent the risk further decreases with higher luminance (CIE 1992).
道路照明的存在能降低夜间道路交通事故的风险,尤其能减少导致行人、骑行者等弱势道路使用者重伤或死亡的事故,并且在一定程度上,风险会随着亮度的提高而进一步降低(CIE 1992)。
The presence of road and public area lighting is also associated with an increase in reassurance that it is safe to walk through or be in a space, and to some extent the reassurance further increases with higher luminance (CIE 2019). The improved reassurance from lighting can reduce the fear of danger expressed often especially by women, and can reduce social isolation of the elderly or those with limited visual or physical capabilities by making it more feasible to be out after dark. Lighting (whether road lighting or the illumination of building facades and landmarks) can make a space more inviting, encouraging the use of and social interactions within an area.
道路和公共区域照明的存在,也能增强人们在相关空间通行或停留时的安全感,并且在一定程度上,安全感会随着亮度的提高而进一步增强(CIE 2019)。照明带来的安全感提升,可以缓解人们(尤其是女性)常有的恐惧感,也能通过提高夜间出行可行性,减轻老年人或其他视觉、行动能力受限者的社会孤立感。照明(无论是道路照明、建筑立面照明还是地标照明)能让空间更具吸引力,从而鼓励人们使用该区域,并促进其中的社交互动。
■ Adverse effects of light at night 夜间照明的不利影响
This Position Statement describes how light at the wrong time and in the wrong place leads to adverse health effects, extending the advice given in the CIE Position Statement on Integrative Lighting (CIE 2024). In an appropriate design, illumination levels directly near road and public area lighting are intended to support human activities, but the resulting illumination penetrating into domestic interior spaces through windows should not have a level that suppresses melatonin production.
本声明阐述了在不恰当的时间和地点使用光照将如何对健康造成不良影响,这是对《CIE综合照明立场声明》(CIE 2024)中相关建议的拓展。在合理的设计中,紧邻道路及公共区域照明的照度水平应能适配人类活动需求,但由此透射进室内居住空间的照度,不应达到抑制褪黑素分泌的水平。
It is important to note that in addition to melatonin suppression, the nuisance from glare, motion, saturated colours and changing illumination levels can also be disruptive to sleep. Adverse effects can be particularly significant when the light is dynamic, such as some advertising panels.
值得注意的是,除抑制褪黑素外,眩光、动态闪烁、饱和色及照度变化带来的不适感,也可能干扰睡眠。当照明具有动态特性时(如部分广告屏),其不利影响可能尤为显著。
■ Mitigation of the adverse effects of light at night夜间照明不利影响的缓解措施
Adverse effects of light at night can be mitigated (whilst not entirely removed) by careful design using suitable products. It is important to understand what light is needed and when. Spaces have a rhythm: daily, weekly, throughout the seasons and throughout the years. A good approach is to light according to the rhythm of use and not simply to light the space without considering how it is used.
通过选用适宜的产品与精细化的设计,可有效缓解(虽无法彻底根除)夜间光照带来的不利影响。关键在于明晰“何时光照”及“何种光照”是必要的。空间具有其内在的节律:它随日夜更替、周次循环,乃至四季流转与岁月变迁而变化。因此,理想的策略应是顺应空间使用的节律进行布光,而非罔顾具体的空间使用方式,单纯地照亮空间。
Lighting design should be undertaken with respect to the capabilities of the human visual system. When the illumination is non-uniform, the observer’s adaptation level is raised in areas of relatively high light levels, making it harder to see details in the dark patch(es) beyond. When the illumination is very uniform, the adaptation level is (more or less) maintained as an observer passes through. Therefore, a good-quality lighting design is more likely to achieve its intended outcomes, possibly at lower overall average illumination levels.
照明设计应充分考量人类视觉系统的生理特性。当照明分布不均时,观察者在相对高亮度区域的适应水平会提升,致使其难以看清周边暗区中的细节。反之,若照明高度均匀,观察者穿行其间时,其视觉适应水平便能基本保持稳定。因此,优质的照明设计往往能以更低的整体平均照度,更有效地达成预期的照明目标。
■ CIE强调,夜间照明应在保障人类安全与活动需求的同时,最大限度减少对健康、生态与文化的负面影响。未来将通过科学研究与技术发展,推动更可持续的照明实践。需进一步开展研究,以更深入地理解夜间人工光对物种与生态系统的影响,并开发更优的对于干扰光与天空辉光的测量方法。
相关文章
最新文章
2025-12-12
2025-12-12
2025-12-12
资讯 | GB 6675《玩具安全》系列强制性国家标准2025版
2025-12-12
2025-12-12
资讯 | 11 月 30 日生效!俄罗斯获单方面暂停联盟其他国家所发证书在俄效力的权力
2025-12-12
2025-12-12
2025-12-12
2025-12-11
媒体中心
最新资讯
联系我们


服务热线
400-116-2629
立讯检测总部
电话:+(86) 0755-8259 1330
邮箱:webmaster@lcs-cert.com
地址:深圳市宝安区沙井街道衙边学子围巨基工业园 A栋1~2楼、C栋3楼

微信公众号
分享行业干货

微信咨询
请备注咨询服务

关注抖音

手机版网站
全国24小时服务热线
di投诉邮箱:customer.complaint@lcs-cert.com 投诉电话tel:18126445450 证书报告验证真伪邮箱: verification@lcs-cert.com
地址:深圳市宝安区沙井街道衙边学子围巨基工业园A栋1~2楼、C栋3楼 手机:18126505465 邮箱:webmaster@lcs-cert.com

 欧盟RED网络安全标准EN 18031
欧盟RED网络安全标准EN 18031
 无线及通信检测
无线及通信检测
 手机通讯产品认证
手机通讯产品认证
 蓝牙BQB产品认证
蓝牙BQB产品认证
 FM/AM产品认证
FM/AM产品认证
 WiFi产品认证
WiFi产品认证
 无线充电产品认证
无线充电产品认证
 对讲机类产品认证
对讲机类产品认证
 基站类认证
基站类认证
 SAR测试
SAR测试
 接收机产品认证
接收机产品认证
 5G NR产品认证
5G NR产品认证
 UWB产品认证
UWB产品认证
 物联网认证
物联网认证
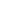
 汽车电子EMC测试
汽车电子EMC测试
 EMC整改
EMC整改
 电磁兼容检测
电磁兼容检测
 电器性能测试
电器性能测试
 EMS测试-辐射抗干扰测试系统(含雷达波)
EMS测试-辐射抗干扰测试系统(含雷达波)
 EMS测试-静电放电
EMS测试-静电放电
 EMS测试-瞬态传导抗干扰测试
EMS测试-瞬态传导抗干扰测试
 EMS测试-便携式发射机抗扰
EMS测试-便携式发射机抗扰
 EMS测试-大电流注入(BCI)测试
EMS测试-大电流注入(BCI)测试
 EMS测试-低频磁场抗干扰测试
EMS测试-低频磁场抗干扰测试
 EMI测试-瞬态传导发射测试系统
EMI测试-瞬态传导发射测试系统
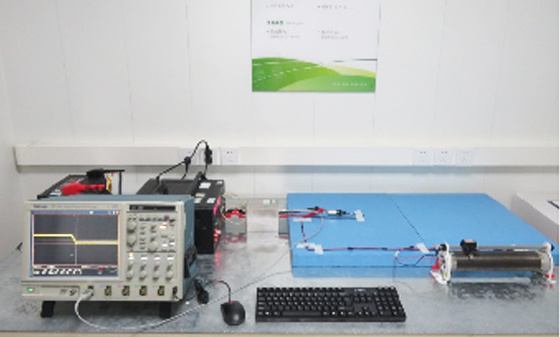 EMI测试-低频磁场发射
EMI测试-低频磁场发射
 EMI测试-辐射发射测试
EMI测试-辐射发射测试
 EMI测试-传导发射测试
EMI测试-传导发射测试
 汽车电子检测
汽车电子检测
 汽车VOC
汽车VOC
 可靠性测试
可靠性测试
 温度冲击试验测试
温度冲击试验测试
 振动测试
振动测试
 仪表台/仪表盘三综合振动试验
仪表台/仪表盘三综合振动试验
 车门内板三综合振动试验测试
车门内板三综合振动试验测试
 遮阳板三综合振动试验测试
遮阳板三综合振动试验测试
 扰流板三综合振动试验测试
扰流板三综合振动试验测试
 汽车前后保险杠三综合振动试验
汽车前后保险杠三综合振动试验
 灯壳/灯罩三综合振动试验
灯壳/灯罩三综合振动试验
 外侧围三综合振动试验
外侧围三综合振动试验
 汽车金属材料测试
汽车金属材料测试
 汽车灯具性能测试
汽车灯具性能测试
 快速温变试验
快速温变试验
 振动试验
振动试验
 振动测试常见问题
振动测试常见问题
 疲劳测试常见问题
疲劳测试常见问题
 高低温测试常见问题
高低温测试常见问题
 传导干扰(CE)-苏州立讯标准
传导干扰(CE)-苏州立讯标准
 电磁辐射耐受测试(RS)-苏州立讯标准
电磁辐射耐受测试(RS)-苏州立讯标准
 电性快速脉冲耐受测试(EFT)-苏州立讯标准
电性快速脉冲耐受测试(EFT)-苏州立讯标准
 电压闪烁测试-苏州立讯标准
电压闪烁测试-苏州立讯标准
 家用电器产品检测
家用电器产品检测
 电器附件产品检测
电器附件产品检测
 家用电器检测
家用电器检测
 PFAS测试介绍
PFAS测试介绍
 MOSH/MOAH矿物油检测服务
MOSH/MOAH矿物油检测服务
 MOSH/MOAH矿物油检测认证报告服务
MOSH/MOAH矿物油检测认证报告服务
 消费品检测服务—WEEE篇
消费品检测服务—WEEE篇
 生态纺织品检测
生态纺织品检测
 食品接触材料检测
食品接触材料检测
 玩具及婴幼儿用品检测
玩具及婴幼儿用品检测
 有害物质检测
有害物质检测
 电子烟检测
电子烟检测
 可靠性HAST介绍
可靠性HAST介绍
 其他检测-铅笔硬度测试
其他检测-铅笔硬度测试
 机械类检测-包装抗压试验
机械类检测-包装抗压试验
 气候环境测试-氙灯老化试验
气候环境测试-氙灯老化试验
 动力储能电池检测认证
动力储能电池检测认证
 消费电子类电池检测认证
消费电子类电池检测认证
 动力电池
动力电池
 轻型电动车辆电池
轻型电动车辆电池
 储能电池
储能电池
 便携式电池
便携式电池
 电池类检测
电池类检测
 电池测试
电池测试
 船舶照明器具检测
船舶照明器具检测
 医疗室内照明COI指数测试
医疗室内照明COI指数测试
 灯具安规检测
灯具安规检测
 灯具能效检测
灯具能效检测
 积分球实验室
积分球实验室
 光生物实验
光生物实验
 光分布测试
光分布测试
 灯具老化测试
灯具老化测试
 灯具IP防水
灯具IP防水
 灯具性能检测
灯具性能检测
 灯具可靠性测试
灯具可靠性测试
 玩具产品检测标准
玩具产品检测标准
 管理体系培训
管理体系培训
 实验室技术培训
实验室技术培训
 实验室工艺咨询
实验室工艺咨询
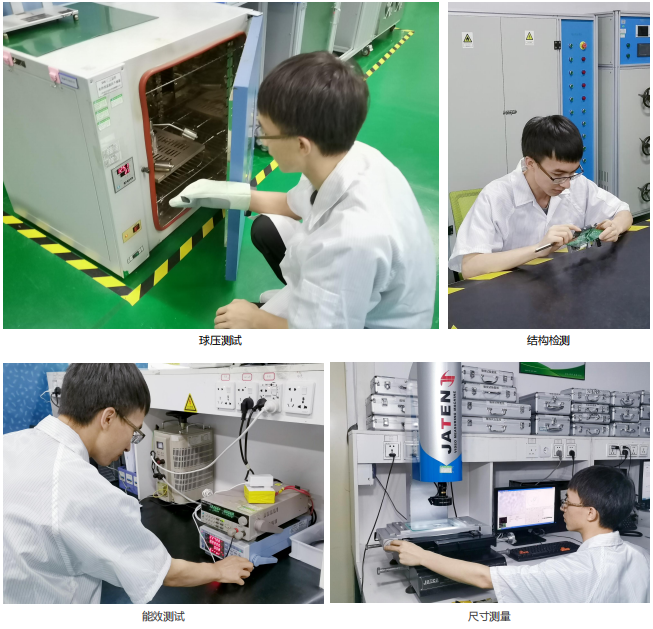 实验室装修建设
实验室装修建设




 扫码咨询
扫码咨询